Docker Image Scan results for bitnami/nginx-intel
Scan performed at 2022-12-12 15:23:07 using the CoGuard CLI
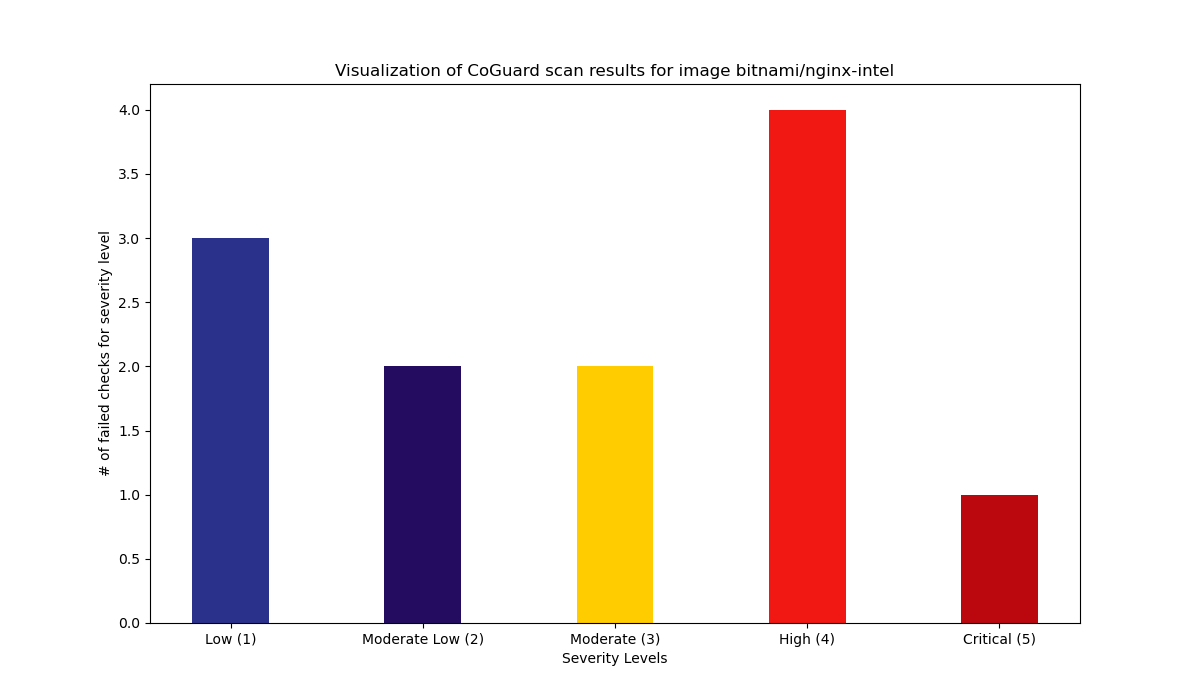
Summary
12 Total failed checks.
5 High / 2 Medium / 5 Low.
Details
| Rule identifier | Severity | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| nginx_enforce_ssl | 5 | SSL should always be enabled, i.e. no cleartext communication. This can be checked in NGINX by adding ssl to the listen arguments. Remediation: Set ssl at the end of every listen directive (unless it is in a path that forwards to an SSL directive).Source: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/configuring_https_servers.html |
| nginx_x_xss_protection_header | 4 | Although being largely replaced nowadays by the Content-Security-Policy header, it is still advisable to add the header X-XSS-Protection to every response to protect older web browsers from potential cross site scripting attacks. Remediation: Ensure that every http block in your NGINX configuration has add_header X-XSS-Protection [VALUE], where value is not 0.Source: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-XSS-Protection |
| nginx_content_security_policy_header_set | 4 | Modern browsers support a header called Content-Security-Policy, where multiple combinations of directives are possible to be set to ensure that the delivered content is not tampered with (e.g. by XSS attacks). This check flags if there is no such header added to an http directive of NGINX.Remediation: Ensure that every http block in your NGINX configuration has the add_header Content-Security-Policy value with some basic rules enabled. Source: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Content-Security-Policy |
| nginx_gzip_off | 4 | Assuming that all communication happens encrypted, one must turn off gzip for compression, since it is otherwise possible to be vulnerable to the so-called BREACH attack. Remediation: Ensure that gzip is never turned on.Source: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html |
| nginx_hsts_header_added | 4 | There is an HTTP response header that instructs the browser to only communicate with the website using HTTPS, the so called HSTS header. This one should be enabled. Remediation: In the http section of the nginx.conf, ensure that there is a directive of the form add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age:<YOUR-VALUE>; includeSubdomains" Source: https://wiki.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Secure_Headers_Project#hsts |
| nginx_limit_simultaneous_connections | 3 | In order to avoid having a single user over-loading the system with parallel connections, NGINX provides a module to limit the parallel connections possible to be opened by a so-called connection zone opened by a user. Remediation: Set the limit_conn key on the top level of the http-block to a value that would fit your specific use case.Source: http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_limit_conn_module.html |
| dockerfile_create_volume_for_var_log | 3 | In linux systems, important operating system logs are stored in the /var/log subfolder. This folder should always be made available to the host through a volume, so that log tracking and log analysis systems can capture them. Remediation: In every Dockerfile, there should be a VOLUME directive which has /var/log as an argument.Source: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/ |
| nginx_disable_content_sniffing | 2 | There is an HTTP response header that makes it harder to perform content sniffing, which is considered a security vulnerability. NGINX can automatically set this header for every response by setting add_header X-Content-Type-Options to nosniff in nginx.conf.Source: https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Content-Type-Options |
| dockerfile_container_healthcheck_parameter | 2 | Dockerfiles have an instruction called HEALTHCHECK. It enables a user to define a command to figure out if the program(s) running inside the container are working properly. It is generally advisable to have healthchecks in place to assist monitoring of running containers. Remediation: Have at least one HEALTHCHECK instruction in your Dockerfile.Source: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/builder/#healthcheck |
| nginx_underscores_in_headers_allowed | 1 | The HTTP standard allows underscores in headers, but NGINX might silently dismiss them. The setting underscores_in_headers on will turn them on for you.Remark: Since the underscores_in_headers_directive is allowed also in server-blocks, but only in very specific ones, we will only pass it if we find it in http-directives. Source: https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/start/topics/tutorials/config_pitfalls/ |
| dockerfile_env_and_arg_defined_and_right_away_used | 1 | When creating Docker images that use environment variables or build arguments, it is advisable to position the ARG or ENV directives close to their actual uses, since otherwise the caching for building the images is not greatly used.Remediation: Every variable defined by an ENV or ARG directive should be used within the next five commands inside the Dockerfile. |
| dockerfile_only_one_definition_per_env_statement | 1 | The ENV statement allows multiple definitions. This should be avoided for readability reasons, as well as pitfalls like variables not being evaluated if defined within the same ENV directive. Remediation: Ensure that every ENV directive has only one assignment. |
Scan performed at 2022-12-12 15:23:07 using the CoGuard CLI